-
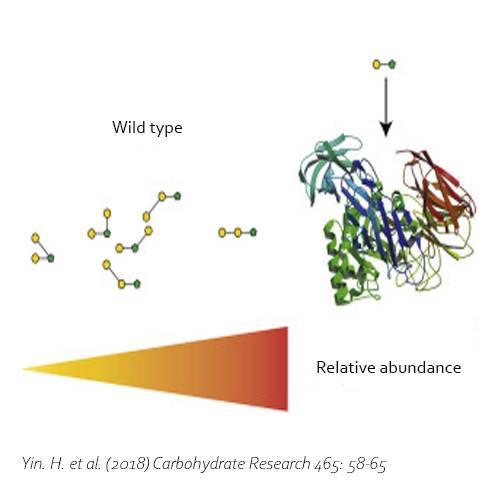
The C-terminally truncated β-galactosidase enzyme of Bacillus circulans ATCC 31382, also known as BgaD-D, is able to synthesize prebiotic galactooligosaccharides (GOS). These products are widely used as a biocatalyst in the food industry, because of their healthy effect on humans. GOS mixtures mimic the prebiotic effects of the human milk oligosaccharides, and therefore are added to infant formula.
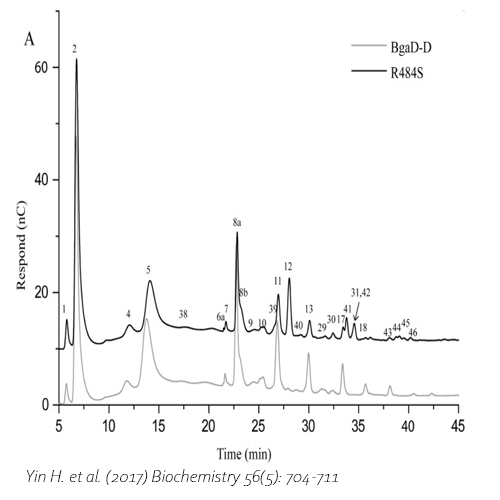
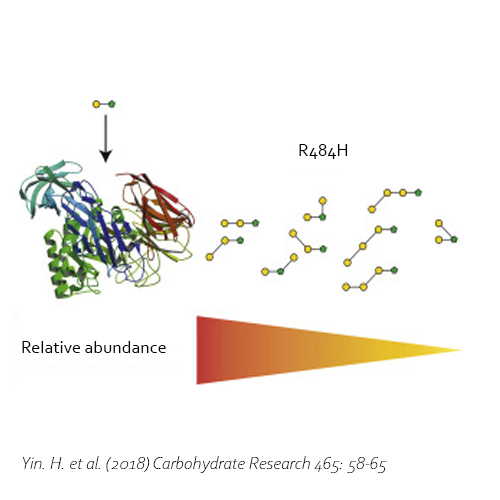
The enzyme BgaD-D mutant R484S displays altered enzyme specificity, leading to new types of GOS products. The GOS mixture produced by the mutant enzyme introduces 14 new structures that were not present in the wild type, 10 of these were completely novel structures (39-46). The other four structures were identified in earlier experiments (38, 29-31). In contrast with the wild type, the GOS products synthesized by BgaD-D mutant R484S presents a carbohydrate mixture showing a majority of β(1→3) and β(1→4) linked galactose on the reducing glucose residue. The products contain both linear and branched structures. Some basic structures are further elongated with β(1→3) and β(1→4)-linked galactose residues, resulting in 3,4-disubstituted galactose residues.
This product is sold for research use only.
-
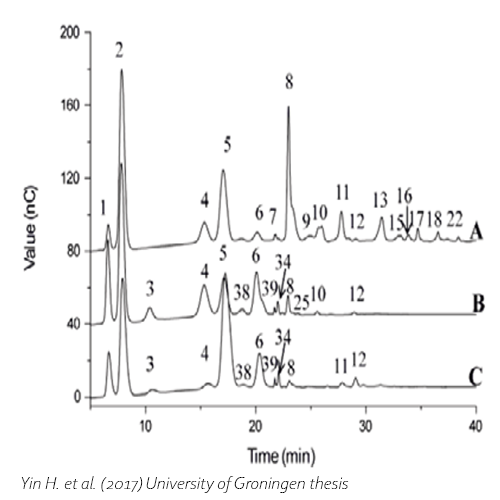
The C-terminally truncated β-galactosidase enzyme of Bacillus circulans ATCC 31382 derived oligosaccharides from lactulose (OsLu). OsLu may act as prebiotic compounds and are potentially resistant to gut digestion.
Five oligosaccharide structures were identified using HPAEC-PAD chromatography, Maldi-ToF-MS, and NMR analysis. The products of the enzyme have a preference for introducing β(1→4) linkages. The trisaccharide β-D-Galp-(1 → 4)-β-D-Galp-(1 → 4)-D-Fru is the most abundant compound in the mixture.
This product is sold for research use only.
-
The C-terminally truncated β-galactosidase enzyme of Bacillus circulans ATCC 31382 mutant R484H synthesizes oligosaccharides from lactulose (OsLu). OsLu may act as prebiotic compounds and are potentially resistant to gut digestion.
In total nine oligosaccharide structures were identified using HPAEC-PAD chromatography, Maldi-ToF-MS, and NMR analysis. Compared with previous studies, six of the characterized structures are novel compounds (i.e. 1, 2a, 5, 6, 7a, and 7b). The products of the R484H mutant enzyme have a preference to introduce β(1→4) and β(1→3) linkages. The trisaccharide β-D-Galp-(1→3)β-D-Galp-(1→4)-D-Fru is major available in the compound mixture. OsLU structures 1-5 were found in both the wild type and R484H mutant. The tetrasaccharides compounds 6 and 7 were only synthesized by the mutant enzyme.
This product is sold for research use only.