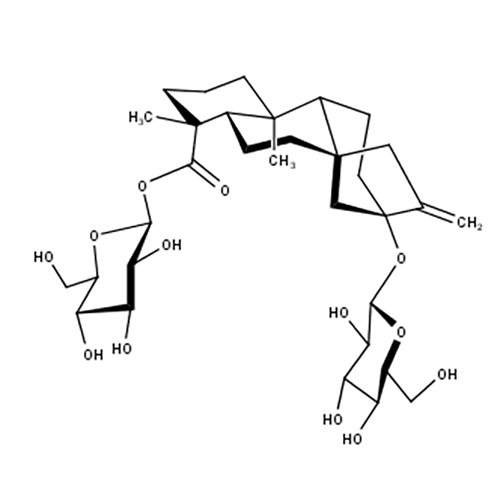
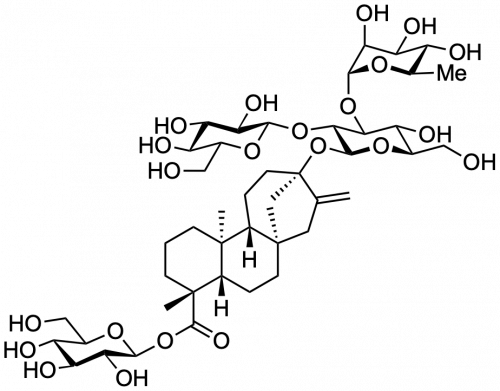
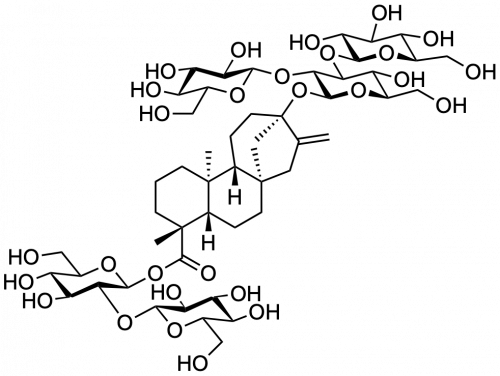
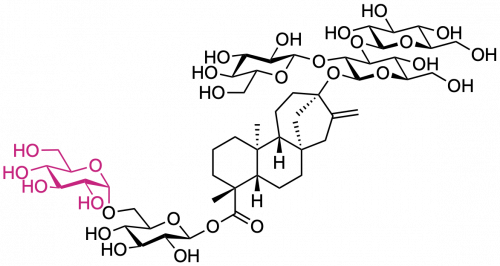
Stevioside glucosylated
Request quote for price
Beschrijving
Stevia rebaudiana (Stevia) is a plant native to South America, the leaves contain sweet components known as steviol and steviol glycosides. These compounds are allowed as food additives in the USA since 2009, and the European market since December 2011. Steviol glycosides are excellent natural alternatives for sucrose and synthetic sweeteners. The main disadvantage of commercial use of steviol glycosides is their bitter lingering aftertaste. The quality and sweetness of the steviol glycosides can be improved via transglycosylation of the C-13 terthydroxyl and the C-19 carboxylic acid functions of the steviol backbone.
The generally recognized as safe (GRAS) bacterium Lactobacillus reuteri 180 enzyme mutant Gtf180-ΔN-Q1140E efficiently α-glucosylates the steviol glycoside stevioside using sucrose as a donor substrate. During the conversion mostly (> 50%) the Glc(β1→C-19 residue of the stevioside is glucosylated, forming an α(1→6) linkage, after which the synthesized Stev-G1 was glucosylated through an α(1→4) linkage, yielding stev-G2. The enzyme formed a mixture of multi-α-glucosylated products whereby the Stev-G2+ is not specifically glucosylated at the C-19, but also at the C13-site.
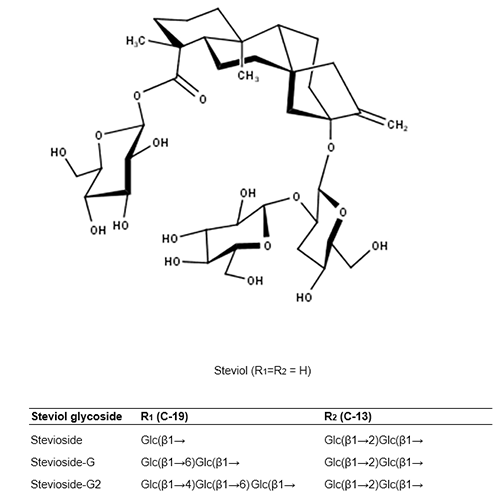
Structure of the aglycone steviol, and the Rebaudioside A residues, occurring in the leaves of Stevia rebaudiana. Glucose (Glc) exists in the pyranose ring form in D configuration.
Devlamynck, T. et al., 2019. Trans-α-glucosylation of stevioside by the mutant glucansucrase enzyme Gtf180-ΔN-Q1140E improves its taste profile. Food Chemistry, 30 1, Volume 272, pp. 653-662. DOI 10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.08.025
Devlamynck, T. N., 2017. Exploring the glucosylation potential of glucansucrases: From enzyme to product, University of Groningen
Extra informatie
| Volume | 10 mg |
|---|